Aviation
Decarbonisation
CTS technology can be used to aid the decarbonisation of aviation in numerous applications across airports.
Enertechnos focuses on gaining large-scale efficiency by improving the way electrical power is supplied, distributed and metered for various uses in airports.
Applications for Aviation
Since 2014, Enertechnos has worked to develop a patented electricity distribution system that delivers more power with lower losses than conventional cable. CTS works far better at higher frequencies and over longer distances than traditional electrical cables. CTS has a major advantage in three areas that are relevant to airports:
- 400Hz Fixed Electrical Ground Power (FEGP)
- 50/60Hz transmission of remote renewable power to the airport
- 85kHz wireless power transfer to allow charging of EVs
Aviation Decarbonisation
All airports face the challenges of decarbonisation and everything that can be done to improve efficiency helps on the road to net zero. While most suppliers focus on selling one piece of efficient technology (LED lights, plug-in EV chargers, etc.), Enertechnos focuses on gaining large-scale efficiency. This efficiency is attained by improving the way that electrical power is supplied, distributed and metered for the various ways it is used in the airport.
Fixed Electrical Ground Power (FEGP): Achieving net-zero for airports
Start with a high-frequency ring main for each terminal.

FEGP: The benefits
- 400Hz distribution direct to every gate from central unit
- Capital savings reducing converters
- Supply ground power to remote stands with CTS
- Reduce use of ground power units (GPU) and auxiliary power units (APU)
- Increased resilience by providing power distribution
- Thermal recovery from centralised power electronics to heat terminals
- 85kHz ring main for wireless electric vehicle charging
The Problem
Aircraft require ground power at 400Hz. It is a requirement to reduce the use of APU and GPU for aircraft on the ground in order to reduce carbon emissions.
- Provision of FEGP is restricted by current cabling technology to a short distance between a 50/400Hz converter and a single aircraft – typically 50-60 metres
- In the event of converter failure, the gate is unserviceable, or the aircraft must use GPU or APU
- A converter is required for every gate – with consequent low utilisation rate
- Difficult to provide FEGP at remote stands because of the distance
Our Solution
Utilise a high-frequency ring main for each terminal (gates and remote stands).
Enertechnos’ CTS makes this possible by using a patented cable topology that facilitates a high-frequency distribution circuit.
- CTS is effective <5,000 metres at 400Hz (cf. < 60 metres for conventional cable)
- Far more cost-effective solution as converter can be shared between multiple aircraft
- Greater resilience to failure compared to one-to-one converter-aircraft configuration
- Far easier to extend to remote stands
- Overall capex and opex reductions from simplified design
- Potential for heat recovery from centralised converter for use in terminal heating
- Facilitates the provision of power for electric PCA units at remote stands
- Enables reduction in GPU/APU use because higher availability, and so reducing the carbon footprint of the airport
- Enables converters to be sited landside for ease of service and maintenance
Wireless Power Transfer (WPT) for Airside Fleet
Obstacles or wide-open spaces?
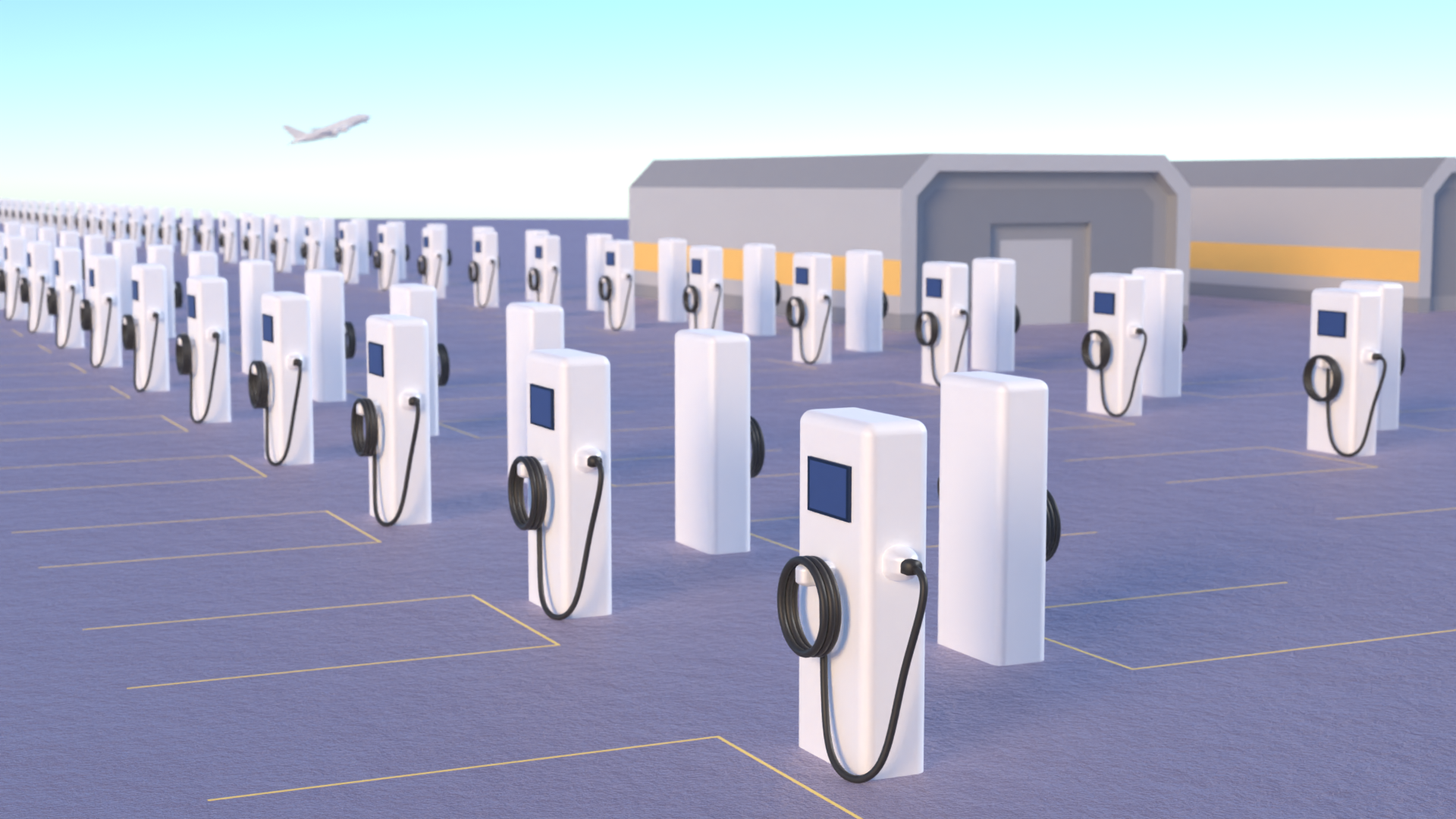

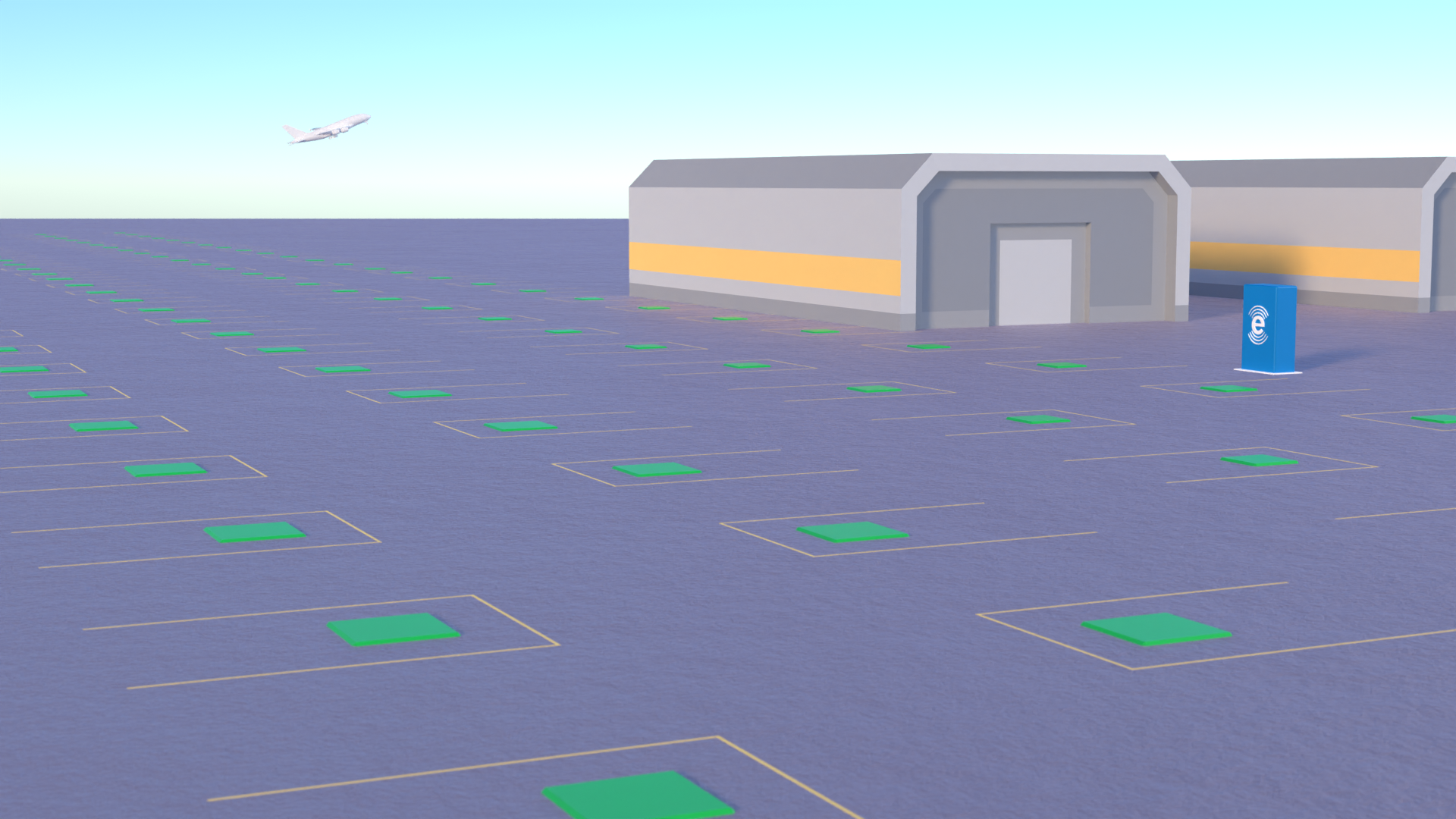
Airside WPT: The benefits
- More space for complex routing of vehicle movements
- Opportunity charging means there is less downtime
- Smaller batteries create vehicle costs of up to 30% less
- No cable breakages or inaccurate connections saves man hours
- Cuts potential collisions with chargers and other vehicles reversing from the unit
- 85kHz ring main from the central converter
- Lower capital expenditure on the frequency converter
- Heat recovery from the central converter to heat terminals
- CTS cable has lower power losses over greater distances than any other cable
Net Zero emissions on the ground is the goal for all airports
With thousands of movements of vehicles 24/7, either owned by the airports, airlines, ground handlers and many outside companies, detailed studies should be made to recommend (conclude) the most efficient and cost-effective ways to achieve these goals.
As a first stage in such a study, Enertechnos will be able to demonstrate how its unique CTS cable can effectively be used with minimal power loss, enabling multiple BEVs to be charged from one central power source with no charging ‘furniture’ allowing easier and safer vehicle movements while achieving zero emission goals.

